In an era where our lives are increasingly dependent on wireless communication, the demand for faster, more reliable, and secure data transmission has never been greater. While Wi-Fi has been the go-to technology for wireless networking for decades, a new contender has emerged on the horizon: Li-Fi. Short for “Light Fidelity,” Li-Fi uses light signals to transmit data, opening up a world of possibilities for the future of wireless networks.
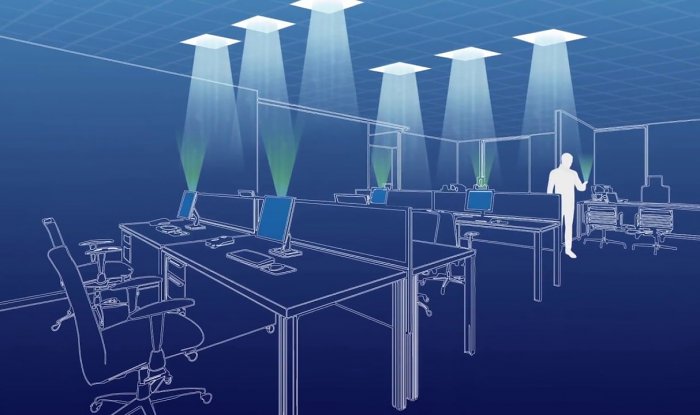
What is Li-Fi?
Li-Fi is a revolutionary technology that uses visible light or infrared signals to transmit data wirelessly. This innovative approach is based on the principle of modulating the intensity of light to encode information. Essentially, Li-Fi turns ordinary LED light bulbs into data-transmitting devices. These bulbs can emit light at such high speeds that the human eye cannot perceive the fluctuations, making it an ideal medium for data transmission.
Speed and Bandwidth
One of the most promising aspects of Li-Fi is its speed. While traditional Wi-Fi operates in the radio frequency spectrum, Li-Fi operates in the visible light spectrum, which offers significantly more bandwidth. This translates into faster data transmission speeds, potentially reaching gigabits per second (Gbps) or even terabits per second (Tbps). Imagine downloading an entire high-definition movie in just a few seconds or transferring massive data files instantly. Li-Fi’s speed could revolutionize how we experience the internet.
Security and Interference
Li-Fi offers a unique advantage in terms of security. Unlike Wi-Fi, which broadcasts signals through walls and can be intercepted by unauthorized users, Li-Fi’s signals are confined within the physical boundaries of the light source. This makes it inherently more secure as it is difficult for outside parties to access the network without physical access to the light source. Li-Fi could become a game-changer for industries requiring high levels of security, such as healthcare, finance, and military applications.
Another benefit of Li-Fi is the reduction of interference. Wi-Fi networks often suffer from interference in crowded environments, resulting in slower speeds and dropped connections. Since Li-Fi relies on light signals, it is less susceptible to interference from neighboring networks or electronic devices, ensuring a more consistent and reliable connection.
Energy Efficiency
Li-Fi not only offers high-speed data transmission but also energy efficiency. LED bulbs, which serve as the backbone of Li-Fi networks, are already known for their energy-saving capabilities. When combined with Li-Fi technology, these bulbs can provide both illumination and data transmission simultaneously, reducing the overall energy consumption of a network. This is a significant advantage for sustainable and environmentally conscious solutions.
Applications of Li-Fi
The potential applications of Li-Fi are vast and varied. Here are some areas where Li-Fi could transform industries and daily life:
1. Healthcare: Li-Fi can enhance the security of patient data in hospitals and clinics while providing high-speed internet access for medical equipment. Surgeons and healthcare professionals could benefit from real-time, high-definition imaging during procedures.
2. Aviation: Li-Fi can offer lightning-fast internet connectivity on airplanes, improving the passenger experience and enabling real-time communication between aircraft and ground control.
3. Smart Cities: Li-Fi could be used for intelligent street lighting systems, enhancing energy efficiency, and enabling data communication between various city infrastructure components, such as traffic lights and sensors.
4. Education: Li-Fi can revolutionize classrooms by providing high-speed internet access without the need for traditional Wi-Fi infrastructure. This could bridge the digital divide in educational settings.
5. Underwater Communication: Unlike radio waves, light signals can penetrate water. Li-Fi could be used for high-speed communication in underwater exploration, maritime industries, and even aquaculture.
6. Retail: Retail stores can use Li-Fi for precise indoor positioning systems, enabling personalized shopping experiences and efficient inventory management.
7. Transportation: Li-Fi can be integrated into vehicles to enable fast and reliable vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication, enhancing road safety and traffic management.
Challenges and Future Developments
While Li-Fi holds great promise, it is not without its challenges. One of the primary limitations is its line-of-sight requirement. Li-Fi signals are blocked by physical obstacles, which means that uninterrupted communication requires a clear line of sight to the light source. This limitation may restrict its use in certain scenarios.
Additionally, Li-Fi technology is still in its infancy, and widespread adoption will require the development of standards and interoperability with existing wireless technologies like Wi-Fi. Researchers and engineers are actively working on addressing these challenges to make Li-Fi a viable option for the future.
In conclusion, Li-Fi represents a thrilling frontier in the world of wireless communication. With its incredible speed, security, and energy efficiency, Li-Fi has the potential to transform a wide range of industries and our daily lives. While challenges remain, ongoing research and development efforts are paving the way for a future where Li-Fi networks coexist with and complement existing wireless technologies, ushering in a new era of connectivity and innovation. As we continue to explore the possibilities of Li-Fi, the future of wireless networks looks brighter than ever.




Leave a Reply